All tools
Boltz-2
Boltz-2 is a biomolecular foundation model for structure and binding affinity prediction. Supports proteins, ligands, DNA, and RNA in multi-component complexes. Automatically scales GPU resources for large complexes. Predicts binding affinity with near-FEP accuracy at 1000x faster speed.
AutoDock Vina
AutoDock Vina is a widely-used molecular docking tool that predicts protein-ligand binding modes using physics-based force fields. Fast, reliable, and the gold standard for structure-based drug discovery.
DiffDock-L
DiffDock-L is a state-of-the-art molecular docking tool that uses diffusion models to predict how small molecule ligands bind to protein targets. It generates multiple binding poses with confidence scores.
GNINA
GNINA is a molecular docking tool that combines traditional physics-based docking with deep learning CNN scoring. It provides accurate binding predictions with confidence scores, optimized for high-throughput virtual screening.
LightDock
LightDock is a protein-protein, protein-peptide, and protein-DNA docking framework using Glowworm Swarm Optimization (GSO). It predicts macromolecular binding modes and interfaces for biological complexes.
ProteinMPNN
Design protein sequences for given backbone structures using deep learning. Fast and accurate inverse folding with state-of-the-art sequence recovery (52.4%).
SolubleMPNN
Specialized model for soluble protein sequence design. Trained exclusively on soluble proteins for optimized performance on cytoplasmic and extracellular proteins.
LigandMPNN
Design protein sequences with atomic context from ligands, metals, and nucleotides. Achieves 63.3% sequence recovery at binding sites, significantly outperforming ProteinMPNN (50.5%).
BoltzGen
BoltzGen is a state-of-the-art AI model for designing protein and peptide binders against any biomolecular target. Using generative diffusion models, it creates novel binders (proteins, peptides, nanobodies) with nanomolar-level binding affinity.
RFdiffusion
RFdiffusion is a state-of-the-art protein structure generation tool that uses diffusion models to design proteins de novo, create binders, scaffold motifs, and generate symmetric oligomers with atomic precision.
AbLang
Restore missing residues in antibody sequences using a language model trained on the Observed Antibody Space (OAS) database. Achieves better restoration than IMGT germlines or ESM-1b while being 7x faster.
AbLang-2
Antibody-specific language model for predicting non-germline residues (NGL) in antibody sequences. AbLang-2 addresses germline bias in existing antibody language models by focusing on somatic hypermutation patterns, enabling more accurate prediction of amino acid likelihoods and generation of context-aware embeddings for antibody sequences.
ADMET-AI
Predict ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity) properties from SMILES strings using machine learning models trained on Therapeutics Data Commons datasets.
Admetica
Predict ADMET (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity) properties from SMILES strings using Chemprop-based machine learning models. Open-source toolkit from Datagrok.
AF-Cluster
Cluster Multiple Sequence Alignments to predict alternative protein conformations with AlphaFold2. Uses DBSCAN clustering to identify sequence subgroups.
Aliphatic Index
Calculate the aliphatic index of protein sequences. A measure of the relative volume occupied by aliphatic side chains, indicating thermostability.
AlphaFlow
Generate protein conformational ensembles using flow matching. Produces multiple diverse structures showing protein flexibility and dynamics.
AlphaFold2
AlphaFold2 via ColabFold for high-accuracy protein structure prediction. Uses MMSeqs2 API for MSA generation with no local databases required. Supports monomer and multimer prediction.

AlphaGenome
AlphaGenome predicts variant effects on gene expression by comparing reference and alternate alleles. Analyze how genetic variants impact regulatory function across up to 1M base pair regions. Uses your own DeepMind API key - no credit cost.
Amino acid composition
Analyze amino acid composition of protein sequences. The tool accepts FASTA sequences and outputs the percentage of each amino acid in the sequence.
AntiFold
Inverse folding for antibody structures. Predicts amino acid sequences compatible with antibody variable domain structures using IMGT numbering. Enables antibody sequence design and optimization while preserving structural integrity.

AutoDock-GPU
GPU-accelerated molecular docking using the AutoDock4 force field. Up to 56x faster than serial AutoDock via CUDA parallelization of the Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm.
BindCraft
Design de novo protein binders using AlphaFold2 backpropagation, ProteinMPNN sequence optimization, and PyRosetta relaxation. BindCraft generates novel protein sequences that bind to user-specified target surfaces.
BioPhi
Antibody humanization and humanness evaluation platform from Merck. Sapiens mode uses deep learning trained on the Observed Antibody Space (OAS) to humanize antibody sequences, while OASis mode evaluates humanness using 9-mer peptide search against human antibody databases.

Brenk filter
Identify toxic, reactive, and pharmacokinetically problematic molecular fragments using structural alert patterns
Chai-1
Chai-1 is a multi-modal foundation model for molecular structure prediction. Predicts 3D structures for proteins, ligands, DNA, RNA, and multi-component complexes with high accuracy.
Chou-Fasman
Predict protein secondary structure using the classic Chou-Fasman algorithm based on amino acid propensities
CleaveNet
AI-powered prediction of protease cleavage sites for matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Analyzes peptide sequences up to 10 residues and outputs z-scores indicating cleavage probability across 17 MMP variants.
Clustal Omega
Perform multiple sequence alignment on protein or nucleotide sequences using the Clustal Omega algorithm.
ColabDock
ColabDock is a protein-protein docking framework that uses AlphaFold2 to predict complex structures guided by experimental restraints from cross-linking mass spectrometry, NMR, or other sources.

CpG Island Finder
Identify CpG islands in DNA sequences using the Gardiner-Garden and Frommer criteria. Analyze GC content, CpG density, and observed/expected ratios.
CSV to FASTA
Convert CSV and TSV files containing sequence data to FASTA format with flexible column mapping and automatic delimiter detection
DiffAb
AI-powered antibody CDR design using equivariant diffusion models. Generates optimized complementarity-determining region (CDR) sequences and structures for antibodies targeting specific antigens. Supports single CDR, multi-CDR co-design, and fixed-backbone sequence design modes.
DLKcat
DLKcat predicts enzyme turnover numbers (kcat values) from protein sequences and substrate structures using deep learning. Combines CNN and GNN architectures for accurate kinetic parameter prediction.

DNA mutator
Apply various mutations to DNA sequences and visualize the changes. Generate point mutations, insertions, deletions, and substitutions with customizable rates.

DNA Shuffle
Shuffle DNA sequences while preserving nucleotide, dinucleotide, or k-mer composition for generating randomized control sequences
DNA to Protein Converter
Translate DNA sequences to protein sequences using genetic code

DNA to RNA converter
Convert DNA sequences to RNA (transcription) - replaces T with U

DNAGenIQ - Random DNA sequence generator
Generate random DNA sequences with customizable length, GC content, and restriction sites for molecular cloning and testing purposes.
DockQ
Assess docking model quality by comparing predicted structures against native references. Calculates DockQ score, iRMSD, LRMSD, fnat, and other quality metrics.
DSSP
Assign protein secondary structure using the DSSP algorithm. The gold standard for hydrogen bond-based structure assignment from coordinates.
DynamicBind
DynamicBind is an AI-powered protein-ligand binding prediction tool that recovers ligand-induced conformational changes from unbound protein structures. It predicts both ligand binding poses and protein conformational changes.
EquiDock
EquiDock is an SE(3)-equivariant graph neural network for rigid protein-protein docking. It predicts binding poses for protein-protein complexes from unbound structures using geometric deep learning. Features keypoint-based confidence scoring, interface residue identification, contact map generation, and multi-pose sampling via random perturbation.
ESM-2
ESM-2 is a 650M parameter protein language model from Meta AI trained on 250M protein sequences. Generate rich sequence representations for downstream tasks like structure prediction, function annotation, and variant effect prediction.
ESM-IF1
Inverse folding with ESM-IF1. Design protein sequences for given 3D backbone structures using a geometric deep learning model. Generate multiple sequence variants optimized for your target structure.
ESMfold
ESMfold is a fast, single-sequence protein structure predictor from Meta AI. Predicts 3D protein structures directly from amino acid sequences without requiring multiple sequence alignments (MSA), making it significantly faster than AlphaFold.
eToxPred
Predict toxicity and synthetic accessibility of small molecules using machine learning. eToxPred combines toxicity risk assessment with synthetic accessibility scoring to help prioritize drug candidates.
EvoDiff
EvoDiff is a diffusion-based protein sequence generation framework from Microsoft Research. It combines evolutionary-scale data with diffusion models to generate novel protein sequences unconditionally, scaffold structural motifs, or fill in disordered regions through inpainting.
EvoPro
Optimize protein binders using genetic algorithms combined with AlphaFold2 fitness evaluation and ProteinMPNN sequence design. EvoPro evolves protein sequences to maximize binding affinity and structural quality through iterative cycles of mutation, selection, and validation.
Extinction coefficient calculator
Calculate the molar extinction coefficient of protein sequences at 280 nm. Used for protein concentration determination by UV spectroscopy.
FASTA splitter
Split large FASTA files into smaller chunks. Divide by sequence count or create individual files for each sequence.
FASTA to FASTQ Converter
Convert FASTA sequence files to FASTQ format with mock quality scores
FASTQ to FASTA converter
Convert FASTQ sequence files to FASTA format
FastTree
Infer approximately-maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees from alignments of nucleotide or protein sequences.
Filter DNA
Clean and filter DNA sequences by removing or replacing non-standard nucleotide characters. Supports multiple filter modes including standard 4 bases, IUPAC ambiguity codes, and custom character sets.

Filter Protein
Clean and filter protein sequences by removing or replacing non-standard amino acid characters. Supports multiple filter modes including standard 20 amino acids, IUPAC codes, and custom character sets.
FoldSeek
Fast protein structure search, comparison, and clustering. Search your structure against 200M+ AlphaFold predictions, compare 2 structures, or cluster up to 2500.
fpocket
Open-source protein pocket detection using Voronoi tessellation and alpha spheres. Identifies ligand binding sites with druggability scores.
GC content calculator
Calculate GC content and nucleotide composition of DNA/RNA sequences. Analyze individual sequences or get combined statistics.

GenBank Feature Extractor
Extract sequence features (CDS, mRNA, gene, etc.) from GenBank files in FASTA format with support for spliced features

GenBank to FASTA Converter
Convert GenBank files to FASTA format
GenMol
GenMol is a generative AI model from NVIDIA that creates novel drug-like molecules using masked discrete diffusion. It generates molecules in SAFE representation format and supports de novo generation, linker design, motif extension, and scaffold decoration.

gmx_MMPBSA
Calculate binding free energies using MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods for protein-ligand, protein-protein, and protein-DNA complexes. Provides detailed energy decomposition and per-residue contributions.

GRAVY
Calculate the GRAVY (Grand Average of Hydropathy) score of protein sequences. Positive values indicate hydrophobic proteins, negative values indicate hydrophilic proteins.
HADDOCK3
HADDOCK (High Ambiguity Driven protein-protein DOCKing) is an integrative modeling platform for biomolecular complexes. It uses experimental data and bioinformatic predictions to guide the docking process, generating accurate protein-protein complex structures.
HighFold
Cyclic peptide structure prediction using HighFold, a modified ColabFold/AlphaFold2 framework with CycPOEM (Cyclic Position Offset Encoding Matrix) for head-to-tail and disulfide bridge constraints.
HMMER
Sensitive sequence homology search using profile hidden Markov models. More accurate than BLAST for detecting remote homologs, ideal for finding evolutionarily distant protein family members.
Hydropathy plot
Generate Kyte-Doolittle hydropathy plots to visualize hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions along protein sequences. Identify transmembrane domains and surface-exposed regions.
Hydrophobicity plot
Generate hydrophobicity plots using 24 different amino acid scales. Visualize hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions for protein analysis, epitope prediction, and membrane protein studies.
HyperMPNN
Design thermostable protein sequences using ProteinMPNN trained on hyperthermophilic organism structures. Generates sequences optimized for improved thermal stability without requiring ligands or additional context.
IgBLAST
Analyze immunoglobulin (antibody) and T cell receptor variable domain sequences. Identifies V/D/J gene segments, delineates CDR regions, and analyzes rearrangement junctions.
IgDesign
Design antibody CDR sequences via inverse folding. Generates complementarity-determining region (CDR) sequences for antibodies targeting therapeutic antigens using deep learning. Optimizes CDR loops (HCDR1, HCDR2, HCDR3) based on antibody-antigen complex structures.
IgGM
IgGM is a generative foundation model for antibody and nanobody design against a target antigen. Supports CDR design, affinity maturation, inverse design, and framework design. Requires an antigen structure (PDB) and antibody sequences with "X" marking positions to design.
ImmuneBuilder
ImmuneBuilder predicts 3D structures of immune receptor proteins including antibodies, nanobodies, and T-cell receptors. Uses specialized models (ABodyBuilder2, NanoBodyBuilder2, TCRBuilder2) optimized for each receptor type with over 100x faster predictions than AlphaFold2.

Instability Index
Calculate the instability index of protein sequences. Values above 40 indicate an unstable protein with a short half-life in vitro.
IPC 2.0 (isoelectric point calculator)
Isoelectric Point Calculator 2.0 - Predict protein/peptide isoelectric point (pI) using 18+ validated pKa scales, SVR models, and deep learning. Supports proteins, peptides, and comprehensive analysis.
IQ-TREE
Build phylogenetic trees using maximum likelihood with automatic model selection (ModelFinder) and ultrafast bootstrap support.

Lead-likeness filter
Screen for lead-like compounds using stricter molecular descriptor criteria than Lipinski or Veber rules for early-stage drug discovery
Lipinski's rule of 5
Lipinski's Rule of Five predicts whether compounds will be orally bioavailable by evaluating molecular weight, LogP, hydrogen bond donors, and acceptors.
MAFFT
Perform multiple sequence alignment using MAFFT (Multiple Alignment using Fast Fourier Transform). Supports multiple algorithms from fast progressive to highly accurate iterative methods.
mBER
Design VHH nanobody binders using AlphaFold-Multimer with structure templates and sequence conditioning. mBER (Manifold Binder Engineering and Refinement) generates novel VHH antibody sequences that bind to user-specified target proteins.
MD Trajectory Analysis
Analyze molecular dynamics trajectories using MDAnalysis. Calculate RMSD, RMSF, and radius of gyration over time. Supports standard topology formats (PDB, GRO, PSF) and trajectory formats (XTC, TRR, DCD, NC).
MDGen
MDGen is a generative AI model for molecular dynamics trajectory generation. Generate physically plausible conformational ensembles from a single protein structure, enabling rapid exploration of protein dynamics without expensive MD simulations.
MiniFold
MiniFold is a fast single-sequence protein structure predictor that is 10-20x faster than ESMFold. It predicts 3D protein structures directly from amino acid sequences without requiring multiple sequence alignments (MSA), making it ideal for rapid structure prediction.
MMseqs2
Ultra-fast sequence search and clustering. 10,000x faster than BLAST for database searches, with powerful sequence clustering capabilities for proteins and nucleotides.

Molecular descriptors
Calculate comprehensive molecular properties and descriptors including molecular weight, LogP, TPSA, aromatic properties, and drug-likeness scores

Molecular weight calculator
Calculate the molecular weight (MW) of protein sequences in Daltons. Supports FASTA format input and batch processing.
MolProbity
Validate protein structure quality with all-atom contact analysis, Ramachandran plots, rotamer assessment, and geometry checks.

MSA Viewer
Interactive viewer for multiple sequence alignments with color-coded residues and consensus sequence
MUMmer4
Rapidly align and compare DNA sequences using MUMmer4 nucmer. Perform pairwise genome comparisons to identify SNPs, indels, and structural variants between reference and query genomes.
MUSCLE5
Perform multiple sequence alignment using MUSCLE5 (MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation). Uses the PPP algorithm for high-quality alignments with support for ensemble generation.
NetSolP-1.0
Predict protein solubility and usability for E. coli expression using ESM protein language models
ODesign
All-atom generative AI for designing protein binders. Specify target binding sites and generate diverse binding proteins with fine-grained control over interaction parameters.

One-to-Three Converter
Convert single-letter amino acid codes to three-letter codes
OpenFold-3
OpenFold-3 is an open-source AI model for biomolecular structure prediction, aiming to reproduce AlphaFold3. Predicts 3D structures for proteins, RNA, DNA, and small molecule ligands with high accuracy.
OpenMM
Run GPU-accelerated molecular dynamics simulations using OpenMM. Simulate protein dynamics, study conformational changes, and analyze stability with industry-standard force fields (AMBER, CHARMM).
ORF Finder
Find all Open Reading Frames (ORFs) in DNA sequences. Searches all six reading frames and supports multiple genetic codes.

PAINS filter
Screen compounds for Pan-Assay INterference patterns that cause false positives in biological assays

PandaDock
Open-source molecular docking platform using physics-based scoring functions. CPU-optimized algorithms achieve sub-angstrom accuracy (0.014A RMSD) without GPU requirements.
ParaSurf
ParaSurf is a state-of-the-art surface-based deep learning model for predicting interactions between antibodies and antigens. It identifies paratope binding sites on antibody structures with high accuracy across multiple benchmark datasets.

PDB to CIF Converter
Convert Protein Data Bank files to Crystallographic Information File format
PDB to FASTA converter
Convert Protein Data Bank files to FASTA sequence format

PDB to MOL2 Converter
Convert Protein Data Bank files to MOL2 molecular format

PDB to SDF Converter
Convert Protein Data Bank files to Structure Data Format

PDB viewer
Visualize and analyze protein structures in 3D using Mol* (molstar), the same viewer used by AlphaFold DB and RCSB PDB
PDB2PQR
PDB2PQR prepares protein structures for electrostatics calculations by adding missing atoms, predicting protonation states using PROPKA, and assigning atomic charges and radii from standard force fields.
PDBFixer
PDBFixer is an OpenMM-based tool used for fixing problems in PDB (Protein Data Bank) files, including adding missing atoms, adding missing residues, and fixing improper formatting.
PepMLM
Design linear peptide binders for target proteins using a target sequence-conditioned masked language model. PepMLM generates peptide sequences optimized to bind specific protein targets based on ESM-2 protein language modeling.

pI Calculator
Calculate the theoretical isoelectric point (pI) of protein sequences. The pI is the pH at which a protein carries no net electrical charge.
PocketFlow
PocketFlow is a structure-based molecular generative model that designs novel drug-like molecules within protein binding pockets. It uses autoregressive flow modeling with chemical knowledge to generate 100% chemically valid, highly drug-like compounds.
PPAP
PPAP (Protein-Protein Affinity Predictor) predicts binding affinity (ΔG and Kd) between interacting protein chains using deep learning with ESM2-3B embeddings. Requires a PDB with 2+ protein chains. Note: This tool is for protein-protein interactions only, not protein-ligand binding.
Primer3
Design PCR primers for DNA sequences with customizable parameters including melting temperature, GC content, product size, and self-complementarity.
PROPKA 3
Predict pKa values of ionizable groups in proteins based on 3D structure. PROPKA calculates the pKa shifts caused by the protein environment for ASP, GLU, HIS, CYS, TYR, LYS, ARG, and terminal groups.
ProstT5
ProstT5 is a protein language model that bidirectionally translates between amino acid sequences and 3Di structural tokens. It enables fast structure-based searches and inverse folding by encoding structural information into a sequence-like representation.
Protein parameters
Calculate protein parameters, including molecular weight, theoretical pI, extinction coefficient, and severla indeces, including instability, aliphatic index, and GRAVY.

Protein stability
Predict protein stability using validated BioPython methods: Instability Index, Aliphatic Index, GRAVY, flexibility analysis, and charge distribution
Protein to DNA converter
Reverse translate protein sequences to possible DNA sequences
Protenix
Open-source AlphaFold 3 implementation by ByteDance for biomolecular structure prediction. Predicts 3D structures for proteins, RNA, DNA, and small molecule ligands with high accuracy.
ProtGenIQ - Random protein sequence generator
Generate random protein sequences with customizable length, composition, and amino acid properties

QEPPI
Quantitative estimate for protein-protein interaction inhibitor potential. Evaluates drug-likeness for compounds targeting PPIs.

Radius of gyration
Calculate the radius of gyration (Rg) for protein structures from PDB files. Supports multiple chains and atom selection options.

Ramachandran plot
Generate Ramachandran plots from PDB structures to analyze protein backbone dihedral angles (phi/psi). Visualize favored, allowed, and outlier regions.

Reverse complement generator
Generate reverse, complement, or reverse-complement of DNA/RNA sequences
RFdiffusion 2
RFdiffusion2 is an atom-level enzyme active site scaffolding tool that generates protein scaffolds around your input motif. REQUIRES an input PDB structure containing the active site residues to scaffold. For ligand-aware design, ligands must be embedded in the input PDB as HETATM records.
RFdiffusion3
All-atom generative diffusion model for protein design with complex constraints. Design binders, enzymes, and symmetric protein assemblies.
RMSD calculator
Calculate Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) between protein structures. Compare a reference PDB against multiple structures with automatic Kabsch alignment.

RNA to DNA converter
Convert RNA sequences to DNA (reverse transcription) - replaces U with T
RNAalifold
RNAalifold computes consensus RNA secondary structure from a multiple sequence alignment. Uses covariation information to improve prediction accuracy for evolutionarily conserved structures.
RNAcofold
RNAcofold predicts the secondary structure of two RNA sequences that interact to form a dimer. Computes the minimum free energy (MFE) structure of the RNA-RNA complex.
RNAdistance
RNAdistance computes the distance between two RNA secondary structures using tree edit distance and base pair distance metrics.
RNAdos
RNAdos designs optimized RNA sequences for target secondary structures using iterative optimization. Produces sequences with better folding properties than single-pass inverse folding.
RNAduplex
RNAduplex computes the hybridization structure between two RNA sequences. Predicts the optimal duplex formation and binding energy.
RNAeval
RNAeval calculates the free energy of an RNA secondary structure for a given sequence. Evaluates if a proposed structure is thermodynamically favorable.
RNAfold
RNAfold predicts RNA secondary structure using minimum free energy (MFE) algorithms. Computes the thermodynamically most stable structure and optional base pair probabilities for RNA sequences.

RNAGenIQ - Random RNA sequence generator
Generate random RNA sequences with customizable types and structural features
RNAinverse
RNAinverse designs RNA sequences that fold into a specified target secondary structure. Inverse folding for RNA sequence design.
RNALfold
RNALfold computes locally stable RNA secondary structures using a sliding window approach. Ideal for long sequences where global folding is computationally infeasible.
RNAplex
RNAplex rapidly predicts RNA-RNA interactions between two sequences. Uses an accessibility-based algorithm for fast identification of potential binding sites.
RNAplfold
RNAplfold computes local base pair probabilities using a sliding window approach. Useful for analyzing accessibility and identifying binding sites in long RNA sequences.
RNAplot
RNAplot generates coordinate data for RNA secondary structure visualization. Computes layout coordinates using the naview algorithm for clear structure display.
RNAsubopt
RNAsubopt enumerates all RNA secondary structures within a specified energy range above the minimum free energy (MFE). Useful for exploring the structural ensemble and identifying alternative conformations.
RNAup
RNAup predicts RNA-RNA interactions considering the cost of opening secondary structures. Accounts for accessibility when computing interaction energy.
RosettaFold3
Open-source structure prediction neural network for proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules. State-of-the-art accuracy with multi-chain support.

SASA calculator
Calculate Solvent Accessible Surface Area (SASA) for protein structures using the Shrake-Rupley algorithm.
ScanNet
Geometric deep learning model for predicting protein binding sites directly from 3D structure. Identifies where proteins interact with other proteins, antibodies, or disordered proteins with high accuracy, including for novel protein folds.

SDF to PDB Converter
Convert Structure Data Format files to Protein Data Bank format
SMINA
SMINA is a fork of AutoDock Vina with enhanced scoring functions, custom scoring support, and 10-20x faster minimization. Ideal for scoring function development, pose refinement, and high-performance docking workflows.
SMRTnet
Deep learning framework for predicting small molecule-RNA interactions using RNA secondary structure. Combines language models, CNNs, and graph attention networks for binding prediction.
SPRINT
SPRINT (Structure-aware PRotein ligand INTeraction) predicts drug-target interactions using co-embedded protein and ligand representations. Screen thousands of compounds against a protein target in seconds.
ThermoMPNN
Predict protein thermostability changes (ΔΔG) for point mutations using a graph neural network. Enables computational saturation mutagenesis screening to identify stabilizing mutations.
Three-to-one converter
Convert three-letter amino acid codes to single-letter codes

Toxicity prediction
Screen compounds for structural toxicity alerts using PAINS, Brenk filters, and custom toxicity patterns. For focused screening, see PAINS Filter, Brenk Filter, or Veber's Rule.
TXT to FASTA converter
Convert plain text sequences to FASTA format - supports DNA, RNA, and protein sequences with automatic cleanup and validation
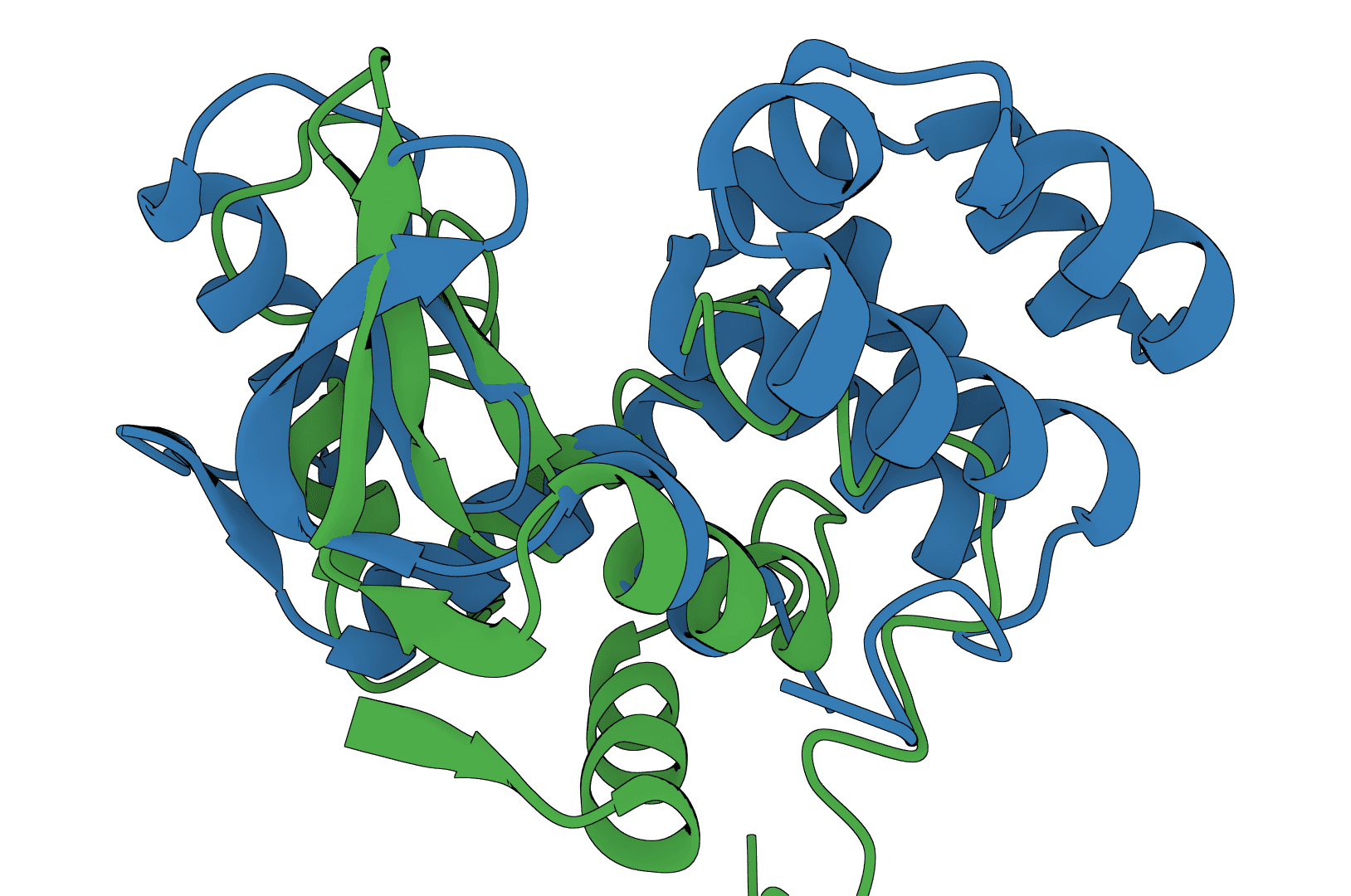
USAlign
USAlign (Universal Structure Alignment) aligns protein, RNA, and DNA structures to compute TM-scores and generate superposed structures. Compare 3D structures to assess structural similarity.

Veber's rule
Veber's Rule predicts oral bioavailability by evaluating molecular weight, LogP, hydrogen bond donors/acceptors, and rotatable bonds
ViennaRNA
ViennaRNA predicts RNA secondary structure using thermodynamic parameters. Computes minimum free energy (MFE) structures, partition functions, and base pair probabilities for RNA sequences.