What is ImmuneBuilder?
ImmuneBuilder is a suite of deep learning models for predicting 3D structures of immune receptor proteins. Developed at the Oxford Protein Informatics Group and published in Communications Biology in 2023, it includes three specialized predictors: ABodyBuilder2 for antibodies, NanoBodyBuilder2 for nanobodies, and TCRBuilder2 for T-cell receptors.
The key advantage over general-purpose structure predictors like AlphaFold2 is speed. By training exclusively on immune receptor structures, ImmuneBuilder achieves over 100x faster predictions while matching or exceeding AlphaFold2's accuracy for CDR loop conformations. This makes it practical for high-throughput screening of antibody libraries and therapeutic antibody engineering workflows where hundreds or thousands of structures need rapid evaluation.
On benchmarks of recently solved antibody structures, ABodyBuilder2 predicts CDR-H3 loops with an RMSD of 2.81 Angstroms—a 0.09 Angstrom improvement over AlphaFold-Multimer. NanoBodyBuilder2 achieves 2.89 Angstrom RMSD on CDR-H3 loops, outperforming AlphaFold2 by 0.55 Angstroms.
How does ImmuneBuilder work?
ImmuneBuilder adapts the structure module architecture from AlphaFold-Multimer with modifications optimized for antibody-like proteins. Each residue is represented as a rigid body defined by 3D coordinates and orientation matrices. Eight sequential update blocks process these representations using Invariant Point Attention layers for structurally-aware feature updates and Backbone Update layers for coordinate refinement.
Ensemble prediction
Rather than relying on a single model, ImmuneBuilder generates four independent structure predictions. The structures are aligned, and the one closest to the ensemble average is selected as the final prediction. Disagreement between ensemble members indicates uncertainty—high variance at a residue position signals low confidence in that region's conformation.
Refinement
Raw neural network outputs occasionally contain steric clashes or stereochemical errors. ImmuneBuilder addresses this with a refinement step using OpenMM and the AMBER14 force field. Restrained energy minimization keeps backbone heavy atoms near their predicted positions while resolving physically implausible geometries.
Training data
ABodyBuilder2 was trained on 7,084 antibody structures from the Structural Antibody Database (SAbDab), filtered for resolution below 3.5 Angstroms with complete variable regions. Separate models were developed for nanobodies and TCRs using analogous curated datasets.
How to use ImmuneBuilder online
ProteinIQ hosts ImmuneBuilder on GPU infrastructure, delivering structure predictions for immune receptors in under a minute without local installation.
Inputs
| Input | Description |
|---|---|
Heavy/Alpha Chain | VH chain (antibody), VHH domain (nanobody), or alpha chain (TCR). FASTA or raw amino acid sequence. |
Light/Beta Chain | VL chain (antibody) or beta chain (TCR). Optional for nanobodies, which are single-domain. |
The tool auto-detects receptor type based on input chains:
- Two chains provided: ABodyBuilder2 (antibody) or TCRBuilder2 (if selected manually)
- One chain provided: NanoBodyBuilder2 (nanobody)
Settings
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Model type | Auto-detect (recommended) selects the appropriate model based on input chains. Override with ABodyBuilder2, NanoBodyBuilder2, or TCRBuilder2 for specific receptor types. |
Auto-detection works reliably for standard inputs. Manual selection is useful when predicting TCRs, which also require two chains but use different chain nomenclature (alpha/beta rather than heavy/light).
Results
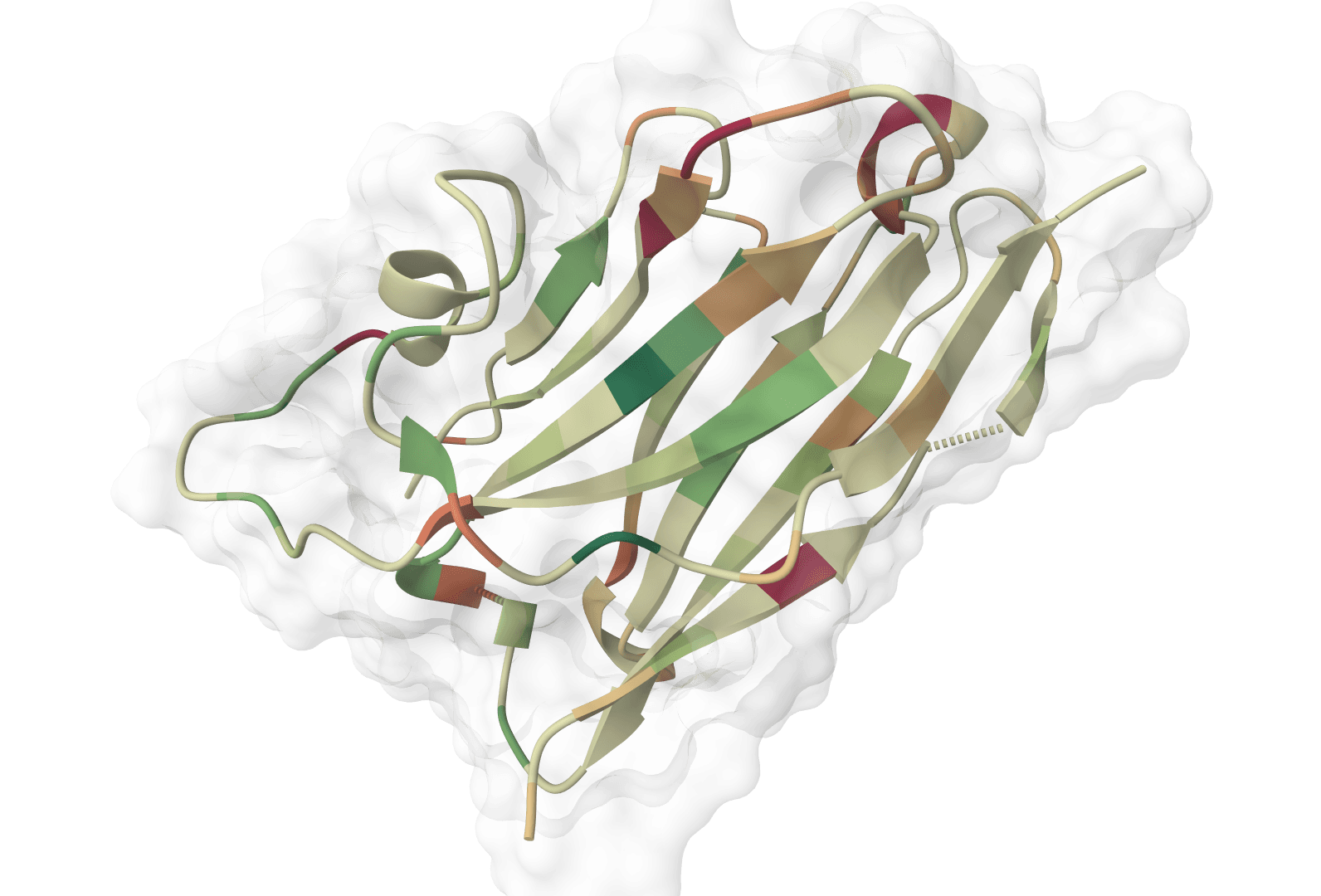
ImmuneBuilder outputs a PDB file containing the predicted 3D structure with per-residue confidence scores stored in the B-factor column. The interactive viewer displays the structure with confidence coloring.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Average confidence | Mean B-factor across all residues. Higher values indicate more reliable predictions. |
Model used | Which ImmuneBuilder variant (ABodyBuilder2, NanoBodyBuilder2, or TCRBuilder2) generated the prediction. |
Total residues | Number of amino acids in the predicted structure. |
Interpreting confidence scores
Confidence scores derive from ensemble agreement—residues where all four models predict similar conformations receive high scores, while variable regions receive lower scores. These scores particularly help identify:
- CDR loops: The complementarity-determining regions, especially CDR-H3, often show lower confidence due to their inherent conformational variability
- Framework regions: Typically show high confidence as they adopt conserved immunoglobulin folds
- Flexible termini: N- and C-terminal residues may show reduced confidence if not constrained by crystal contacts in training structures
Applications
ImmuneBuilder addresses several needs in antibody and immune receptor research:
- Therapeutic antibody development: Rapid structural modeling of antibody candidates to assess CDR conformations, identify potential liabilities, and guide engineering decisions
- Antibody library screening: High-throughput structure prediction for large antibody repertoires where AlphaFold2's speed would be prohibitive
- Nanobody design: Single-domain antibody engineering benefits from NanoBodyBuilder2's specialized training on VHH structures
- TCR structural analysis: Understanding T-cell receptor conformations for immunotherapy applications and epitope-TCR interaction studies
Limitations
CDR-H3 prediction remains challenging across all methods. This hypervariable loop adopts diverse conformations depending on antigen context, and both experimental and computational approaches show limitations. ImmuneBuilder's 2.81 Angstrom RMSD for CDR-H3 represents state-of-the-art performance but may not capture all relevant conformational states.
The models were trained on crystallographic structures, which represent static snapshots. Dynamic conformational changes upon antigen binding or other induced-fit mechanisms are not captured.
Performance may degrade for antibodies with unusual features not well-represented in training data, such as very long or short CDR loops, unusual disulfide patterns, or engineered modifications.
Related tools
- AlphaFold 2: General protein structure prediction; use for non-immune proteins or when ImmuneBuilder inputs are not available
- ESMFold: Fast single-sequence structure prediction without MSA; suitable for rapid screening when ImmuneBuilder's immune-specific training is not required
- IgBLAST: V/D/J gene annotation and CDR identification; useful for preparing sequences before structure prediction
- BioPhi: Antibody humanization and humanness scoring; complements structural analysis for therapeutic development
- AbLang: Antibody language model for restoring missing residues; can prepare incomplete sequences for ImmuneBuilder